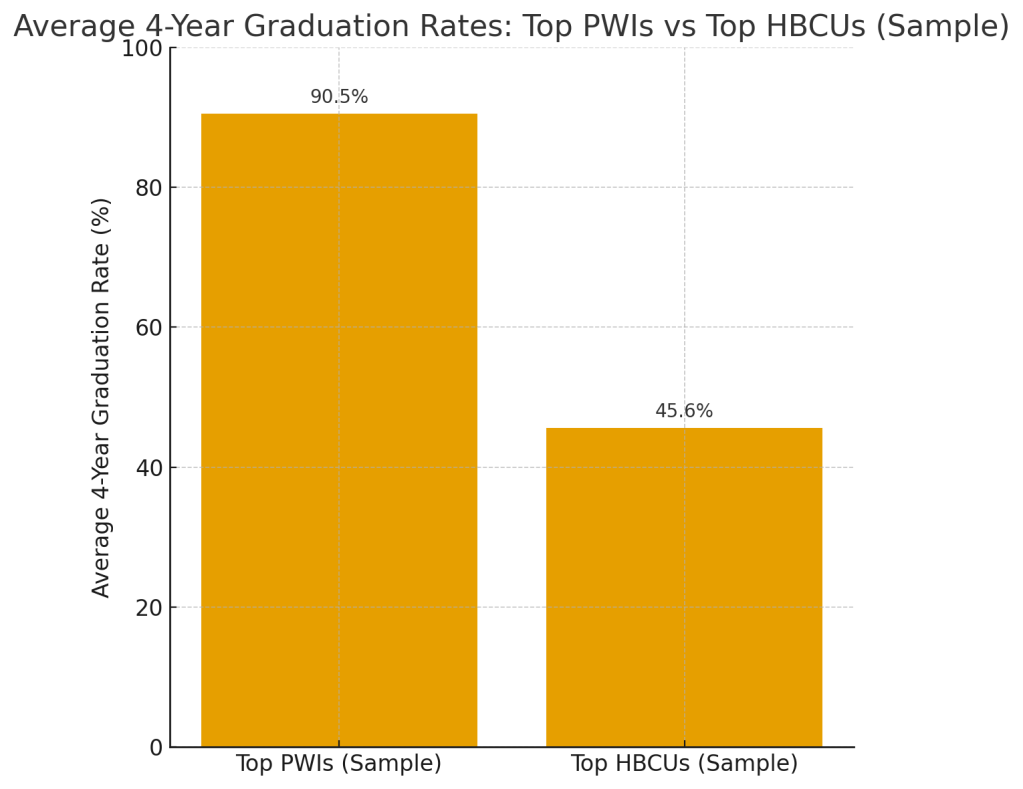
The four-year graduation rate is often presented as a benign statistic tucked inside higher education reports, but for institutions serving African America, it is not benign at all. It is the lever on which long-term wealth, institutional survival, and multigenerational stability subtly depend. Wealthy universities treat the four-year graduation rate not as an outcome but as an engineered product, backed by endowment might, operational discipline, and capital-rich ecosystems. Their students finish on time because the institution ensures they are shielded from interruption. Meanwhile, HBCUs navigate a different reality: the same students who possess the intellectual capacity to thrive are too often delayed not by academics but by the economic turbulence that disproportionately defines their journey. It is here between the idea of talent and the machinery of capital that the four-year graduation rate becomes a revealing measure of African America’s structural position in the American economic hierarchy.
A delayed degree carries a cost structure that compounds aggressively. Extra semesters are not simply tuition bills; they are opportunity-cost accelerants. A student who graduates at 22 enters the workforce two to three years ahead of a peer who reaches the finish line at 24 or 25. Those early earnings fund retirement accounts earlier, compound longer, support earlier homeownership, and create the financial runway that future philanthropy relies upon. For African American students who statistically begin college with fewer financial reserves and exit with higher student debt those lost years are wealth years. They represent not only diminished individual prosperity but the slowed creation of a donor class that HBCUs and other African American institutions depend on to build endowment strength and institutional sovereignty.

Endowments, which serve as the economic lungs of a university, breathe differently depending on how quickly their alumni progress into stable earning years. A university that graduates students in four years rather than six gains an alumni base that stabilizes earlier, saves earlier, invests earlier, and gives earlier. A philanthropic ecosystem is essentially a long-term consequence of time management: the more years an alumnus spends debt-free and employed, the more predictable their giving pattern becomes. Elite institutions leverage this fact elegantly. HBCUs, despite producing extraordinary alumni under significantly harsher financial conditions, remain constrained by the delayed timelines imposed by student financial fragility.
Financial fragility is a central explanatory variable in the HBCU graduation gap. It is not uncommon for a student to miss a semester because of a $300 balance or a transportation breakdown that derails their schedule. In the broader American economic system, such modest shocks rarely jeopardize a wealthy student’s trajectory. But within the HBCU ecosystem, they represent the sharp edges of institutional undercapitalization meeting the exposed nerves of household vulnerability. The four-year graduation rate is therefore not simply a metric of academic navigation but a map of where the Black household economy intersects with American higher education’s structural inequities.
This makes alumni involvement not a sentimental tradition but an economic necessity. Alumni can narrow the financial fragility gap more efficiently than any other stakeholder group. Microgrant funds, even modestly capitalized, are capable of eliminating the most common disruptions that extend time-to-degree. A $250 emergency grant can protect $25,000 in long-term student debt. A $500 intervention can guard a student’s four-year trajectory and thus preserve two additional years of post-graduation earnings that ultimately benefit both the graduate and the institution’s future endowment. Alumni-funded tutoring, advising enhancements, STEM support programmes, and paid internships create artificial endowment-like effects: stabilizing student progression even when the institutional endowment itself is undersized.

Yet HBCU alumni cannot focus solely on the university years if the goal is a structurally higher four-year graduation rate. The process begins far earlier within K–12 systems that shape academic readiness long before students set foot on campus. The elite institutions that boast 85–95 percent on-time graduation rates are drawing from K–12 ecosystems with intense capital saturation: high-quality teachers, advanced coursework, stable households, well-funded enrichment programmes, and neighborhoods that function as multipliers of academic preparedness. HBCU alumni have an opportunity to influence this pipeline through investments that are often modest in individual scope but transformational in aggregate impact. Funding reading centres, coding clubs, college-prep academies, robotics labs, literacy coaches, and after-school tutoring programmes plants the seeds of future four-year graduates years before college entry.
Indeed, a strong K–12 foundation reduces the need for remedial coursework, accelerates major declaration, strengthens performance in gateway courses like calculus and biology, and diminishes the likelihood that students need extra semesters to satisfy graduation requirements. When alumni support dual-enrollment initiatives, sponsor early-college programmes, or build partnerships between HBCUs and local school districts, they enlarge the pool of college-ready students whose likelihood of completing on time is structurally higher. In this sense, investing in K–12 is not philanthropy it is pre-endowment development.
The economic implications of strengthening both ends of the education pipeline are enormous. A 20–30 percentage-point improvement in four-year completion rates across the HBCU ecosystem would reduce student loan debt burdens by billions, accelerate African American household wealth accumulation, raise the number of alumni earning six-figure incomes before age 30, and increase the philanthropic participation rate across Black institutions. Over decades, such shifts ripple outward: stronger alumni lead to stronger HBCUs, which lead to stronger civic, cultural, and economic institutions in African American communities, which themselves create more stable families, more prepared K–12 students, and more future college graduates. The system feeds itself when time is efficiently managed.
In the HBCU Money worldview, where institutional power is the only reliable safeguard against structural marginalization, time-to-degree represents one of the clearest and most overlooked levers of collective economic advancement. In a Financial Times context, the four-year graduation rate appears as a liquidity indicator—showing how quickly an institution converts educational investment into economic output. In The Economist’s framing, it reveals the mismatched capital structures between wealthy universities and historically underfunded ones, and how those mismatches reproduce inequality in slow, quiet, compounding increments.
For African America, the conclusion is unmistakable. The four-year graduation rate is not merely a statistic. It is a wealth mechanism. It is an endowment accelerator. It is an institutional survival tool. And it is a community-level economic strategy that begins in kindergarten and culminates with a diploma. If HBCU alumni wish to see their institutions strengthen, their communities accumulate wealth, and their young people enter the economy with maximum velocity, then they must make both K–12 investment and four-year graduation obsession-level priorities. Institutions rise with the financial stability of their graduates. Ensuring those graduates complete degrees on time is one of the most effective—and least discussed—strategies available for building African American institutional power across generations.
A Tale of Two Virginias:
A revealing contrast in American higher education can be observed by examining two institutions that sit just 120 miles apart: Virginia State University (VSU) and the University of Virginia (UVA). NACUBO estimates VSU’s endowment at approximately $100 million for around 5,000 students, producing an endowment-per-student of roughly $20,000. According to U.S. News, VSU graduates 27% of its students in four years. UVA, one of the most heavily capitalized public universities in the world, possesses an endowment of roughly $10.2 billion for about 25,000 students, an endowment-per-student of approximately $410,000, more than twenty times the capital density VSU can deploy. Its four-year graduation rate stands at 92%.
The gulf between the two institutions reflects not a difference in student talent but a difference in institutional resource density and shock absorption capacity. A VSU student must personally carry far more academic and financial fragility. A single $300 expense can knock them off their semester plan. A delayed prerequisite can add a year to their degree. Limited advising bandwidth means problems are often discovered only after they have already extended time-to-degree. UVA faces the same categories of issues, but its endowment, staffing, and operating budgets act as buffers absorbing shocks before they disrupt academic progress.
Endowment-per-student, therefore, is not merely a balance-sheet statistic; it is a proxy for how much risk the institution can carry on behalf of its students. UVA carries most of the risk. VSU students carry most of their own. UVA’s 92% four-year graduation rate is a reflection of institutional cushioning. VSU’s 27% rate reflects its absence.
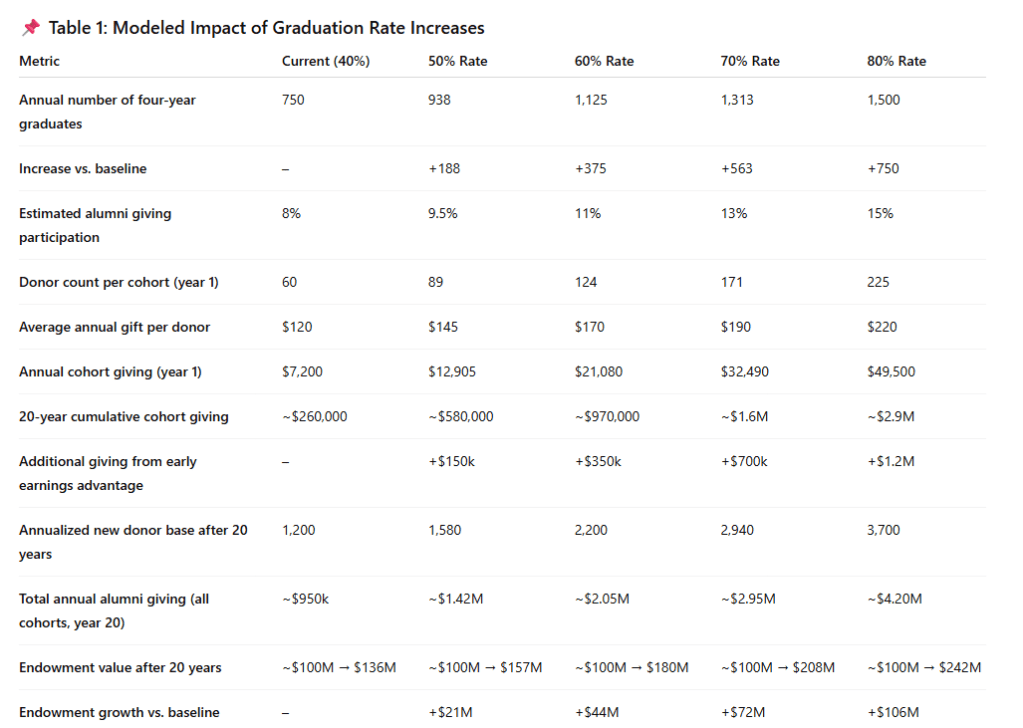
Yet to understand the true economic cost of the graduation gap, it is useful to model what would happen if VSU improved its four-year graduation rate—first to a plausible mid-term target such as 50%, and then to a UVA-like 90%. Both scenarios dramatically change the trajectory of the institution.
Assume that VSU today produces roughly 1,350 graduates every four years (based on a 27% rate). If it increased its four-year graduation rate to 50%, VSU would instead graduate 2,500 students every four years, an increase of 1,150 additional on-time graduates, each entering the workforce two years earlier, with lower student debt, earlier retirement contributions, earlier homeownership, and earlier philanthropic capacity. Even if only a modest fraction of these additional graduates contributed $50–$150 annually to VSU’s endowment, the compounding effect across 20 years would be substantial. Under conservative assumptions with basic donor participation growth and average returns of 7% VSU’s endowment could plausibly grow from $100 million to $155–$170 million over two decades, powered largely by the increased velocity and increased number of earning alumni.
Now consider the UVA-like scenario. A four-year graduation rate of 90% at VSU would mean roughly 4,500 on-time graduates every four years or over three times the current output. This scale of early, debt-lighter graduates would fundamentally transform VSU’s financial ecosystem. Even minimal alumni participation say, 12–15% giving $100–$200 annually would translate into millions in annual recurring contributions. Over two decades, with investment returns compounding, VSU’s endowment could grow not to $150 million but potentially to $300–$400 million, depending on participation rates and gift sizes. That would triple the institution’s financial capacity without a single major donor campaign, capital campaign, or extraordinary windfall. The key variable is simply graduation velocity.
This comparison illustrates a broader truth: endowment growth is not just a function of investment strategy but of how quickly a university converts students into earning alumni. A student who graduates at 22 gives for 40–50 years. A student who graduates at 25 gives for 30–35 years. A student who drops out does not give at all. VSU’s current 27% four-year graduation rate is not merely an academic statistic—it is an endowment drag factor. UVA’s 92% rate is an endowment accelerant.
The financial distance between the two universities appears vast, but it is governed by a formula that HBCUs can influence: more on-time graduates → more early earners → more consistent donors → more endowment growth → more institutional cushioning → more on-time graduates. VSU today sits at the fragile end of this cycle. A graduation-rate increase to 50% would move it into a position of stability. A leap to 90% would place it into an entirely different institutional category—one where it begins to accumulate capital in the same compounding manner that allows institutions like UVA to weather downturns, attract top faculty, and protect students from the shocks that so often derail academic momentum.
VSU cannot replicate UVA’s wealth in the short term. But by increasing on-time graduation, it can replicate the mechanism through which wealthy universities become wealthier. And that mechanism—graduation velocity—is one of the few levers fully within reach of alumni, leadership, and institutional partners.
Here are four strategic, high-impact actions HBCU alumni associations or chapters can take to directly raise four-year graduation rates and strengthen institutional wealth:
1. Create a Permanent Emergency Microgrant Fund (The “$300 Fund”)
Most delays in graduation arise from small financial shocks:
balances under $500, transportation failures, book costs, or housing gaps.
Alumni chapters can formalize a permanent, locally governed microgrant fund offering rapid-response support (48–72 hours).
A chapter raising just $25,000 per year can prevent dozens of delays, each shielding students from additional semesters of debt and protecting the institution’s future alumni giving pipeline.
This is low-cost, high-yield institutional intervention.
2. Fund Paid Internships and Alumni-Mentored Work Opportunities
Students who work long hours off campus are more likely to fall behind academically, switch majors repeatedly, or extend enrollment.
Alumni chapters can create paid internships, stipends, or alumni-hosted part-time roles tied directly to students’ majors.
Each position:
- reduces the student’s financial burden
- keeps them academically aligned
- accelerates pathways to stable post-graduate employment
This lifts graduation rates and increases alumni earnings—expanding the future donor base.
3. Build K–12 Pipelines in Local Cities That Feed Directly Into HBCUs
Four-year graduation begins long before freshman year.
Alumni chapters can adopt 2–3 local schools and support:
- literacy acceleration programs
- SAT/ACT prep
- dual enrollment partnerships
- STEM and robotics clubs
- early-college summer institutes hosted by their own HBCUs
Better-prepared students require fewer remedial courses, retain majors longer, and graduate on schedule, raising institutional performance and future endowment sustainability.
This is pre-investment in the future alumni base.
4. Pay for Summer Courses After Freshmen Year to Build Early Credit Momentum
After their first year, many students fall off the four-year pace due to light credit loads, failed gateway courses, or sequencing issues that a single summer class could easily correct. Yet for many HBCU students, summer tuition—often just one or two courses—is financially out of reach.
Alumni chapters can establish a Freshman Summer Acceleration Grant to pay for up to two summer course immediately after freshman year, allowing students to:
close early credit gaps,
retake or accelerate critical prerequisites,
reduce future semester overloads,
create a credit cushion for unexpected disruptions,
stay aligned with four-year degree maps.
A small investment of summer tuition produces an outsized institutional return: students enter sophomore year on pace, avoid bottlenecks in upper-level coursework, and dramatically increase their likelihood of graduating in four years. This is an early-stage compounding effect—protecting momentum before delays become expensive and permanent.
Disclaimer: This article was assisted by ChatGPT.




Charlamagne Tha God & Jemele Hill: The Debate They Both Got Right and Wrong
“If you don’t own anything, you don’t have any power.” — Dr. Claud Anderson
When Charlamagne Tha God proclaimed, “Wake your ass up and get to trade school!” after NVIDIA’s CEO Jensen Huang suggested that the next wave of American millionaires will come from plumbers and electricians, he was not simply shouting into the void. He was echoing a national frustration, one rooted in the rising irrelevance of a degree-driven economy that no longer guarantees stability or wealth. Student debt has grown into a generational shackle, corporate loyalty is dead, and a working class once promised a middle-class life for earning a degree has found itself boxed out of the very prosperity it was told to chase. Charlamagne’s message resonated because trades feel like a lifeboat in an economy where white-collar work has become overcrowded, uncertain, and increasingly automated. But Jemele Hill’s response, “There’s nothing wrong with getting a trade, but the people in the billionaire and millionaire class aren’t sending their kids to trade schools” was the kind of truth that punctures illusions. She was not critiquing the trades; she was critiquing the belief that skill, in isolation from ownership, can produce power.
Her point hits harder within African America because our community has historically been guided into labor paths whether trade or degree that position us as workers within someone else’s institutions. It is not a coincidence. As HBCU Money examined in “Washington Was The Horse And DuBois Was The Cart”, the historical tension between industrial education and classical higher learning was never about choosing one or the other. It was about sequencing. Booker T. Washington understood that African America first needed an economic base, a foundation of labor mastery and enterprise capacity. W.E.B. DuBois emphasized intellectual development and leadership cultivation. But Washington was right about one thing: without an economic foundation, intellectual prowess has no institutional home. And without institutional homes, neither the trade nor the degree can produce freedom. African America today is suffering because we abandoned Washington’s base-building and misinterpreted DuBois’s talent development as permission to serve institutions built by others.
Charlamagne’s trade-school enthusiasm fits neatly into Washington’s horse, the practical skill that generates economic usefulness. But Hill’s critique reflects DuBois’s cart understanding how society actually distributes power. The mistake is that neither Washington nor DuBois ever argued that skill alone, or schooling alone, was enough. Both ultimately pointed toward institutional ownership. Neither wanted African Americans to remain permanently in the labor class. The trades were supposed to evolve into construction companies, electrical firms, cooperatives, and land-based enterprises. The degrees were supposed to evolve into banks, research centers, hospitals, and political institutions. What we actually did was pursue skills and credentials not power. We mistook competence for control.
This is why the trades-versus-degrees debate is meaningless without ownership. Becoming a plumber or an electrician provides income, but not institutional leverage. Becoming a lawyer or an accountant provides upward mobility, but not institutional control. A community with thousands of tradespeople and thousands of degreed professionals but without banks, construction firms, land ownership, hospitals, newspapers, media companies, sovereign endowments, or venture capital funds is still a community of laborers no matter how educated or skilled.
This structural truth becomes even clearer when viewed through the lens of how the wealthiest Americans use education. HBCU Money’s analysis, “Does Graduate School Matter? America’s 100 Wealthiest: 44 Percent Have Graduate Degrees”, observes that while nearly half of America’s wealthiest individuals do hold graduate degrees, the degrees themselves are not the source of wealth. They are tools of amplification. They work because the individuals earning them already have ownership pathways through family offices, endowments, corporations, foundations, and networks that translate education into power. Graduate school matters when you have an institution to run. It matters far less when your degree leads you into institutions owned by others.
African American graduates rarely inherit institutions; they inherit responsibility to institutions that do not belong to them. So the degree becomes a ladder into someone else’s building. And trades, stripped of the communal ownership networks they once fed, become a ladder into someone else’s factory, subcontracting chain, or municipal maintenance operation. We are always climbing into structures that someone else owns.
This cycle was not always our trajectory. The tragedy is that HBCUs once created institutional ecosystems where skill and knowledge were used to build African American economic capacity—not merely transfer it outward. As HBCU Money argued in “HBCU Construction: Revisiting Work-Study Trade Training”, many HBCUs historically operated construction, carpentry, and trade programs that literally built the campuses themselves. Students learned trades while constructing residence halls, dining facilities, barns, academic buildings, and infrastructure that the institution would own for generations. That model kept money circulating internally, built hard assets, created institutional wealth, and established capacity for African American contracting firms. It produced not just skilled laborers it produced apprentices, foremen, entrepreneurs, and business owners. It produced Washington’s economic foundation.
The abandonment of these models created a void. Trades became disconnected from institutional development. Degrees became pathways to external employment. And HBCUs which once trained students to build institutions were transformed into pipelines feeding corporate America and federal agencies that rarely reinvest into African American institutions at scale. This is why the trade-school-versus-college debate is hollow. Both are simply skill paths. Without ownership, both lead to dependence.
Charlamagne’s sense of urgency comes from watching African American millennials and Gen Z face an economy with fewer footholds than their parents had. But urgency alone cannot produce strategy. Hill, consciously or unconsciously, pointed out that the wealthy understand something we have not fully grasped: the ultimate purpose of skill, whether manual or intellectual, is to strengthen one’s own institutional ecosystem not someone else’s. The wealthy do not send their children to college to find jobs; they send them to college to learn to oversee family enterprises, influence policy, govern philanthropic endowments, and maintain social capital networks. A wealthy family’s electrician child does not go into electrical maintenance he goes into managing the electrical firm the family owns.
This is the distinction African America must confront. We keep choosing roles instead of building infrastructure. We choose jobs. We do not choose institutions. We chase wages. We do not chase ownership. This is not because African Americans lack talent or ambition. It is because integration disconnected African America from its economic development logic. In the push to integrate into white institutions, we abandoned the very institutions that anchored our communities—banks, hospitals, insurance companies, manufacturing cooperatives, and HBCU-based work-study and trade ecosystems.
The future requires rebuilding a Washington-first, DuBois-second model. The horse that is the economic base must return. The cart that is the intellectual class must attach to institutions that the community owns. Trades should feed African American contracting firms, electrical cooperatives, and infrastructure companies that service Black communities and employ Black workers. Degrees should feed African American financial institutions, research centers, HBCU endowments, political think tanks, and venture funds. Every skill, trade, or degree must be tied to institutional expansion.
Otherwise, we will continue mistaking income for empowerment, education for sovereignty, and representation for ownership. Trade or degree, individual success means little when the community remains institutionally dependent. Wealth that dies with individuals is not power; it is a temporary advantage. Power is continuity. Power is structure. Power is ownership.
The choice before African America is not between trade and degree. It is between labor and ownership. No skill, not plumbing, not engineering, not medicine, not law creates power without institutions. We are not lacking talented individuals; we are lacking the institutional architecture that turns talent into sovereignty.
Charlamagne spoke to survival. Hill spoke to structure. Washington spoke to foundation. DuBois spoke to leadership. The synthesis of all four is the path forward. Without institutions, African America will always remain the labor in someone else’s empire even when the labor is highly paid, well-trained, and excellently credentialed. Only ownership transforms skill into power, and without rebuilding our institutional ecosystem, we will continue to debate trades and degrees while owning neither the companies nor the universities.
Ownership is the only path. Without it, neither the horse nor the cart will ever move.
Disclaimer: This article was assisted by ChatGPT.
1 Comment
Posted in Uncategorized
Tagged African American cooperative economics, African American economic independence, African American entrepreneurship, African American institutional ownership, Black community ownership, Black construction industry, Black institutional power, black wealth building, Black-Owned Businesses, Booker T. Washington economic philosophy, charlamagne tha god, Charlamagne Tha God commentary, economic empowerment African America, HBCU economic strategy, HBCU Endowment Growth, HBCU trade training, institutional sovereignty Black community, jemele hill, Jemele Hill analysis, trades vs degrees debate, W.E.B. DuBois leadership development, wealth gap analysis