“When I’m asked about the relevance to Black people of what I do, I take that as an affront. It presupposes that Black people have never been involved in exploring the heavens, but this is not so. Ancient African empires – Mali, Songhai, Egypt – had scientists, astronomers. The fact is that space and its resources belong to us, not to any one group.” – Mae Jemison
The United States government’s recent decision to withdraw its only research vessel from Antarctica represents more than a logistical setback for American science it signals a historic opportunity for Historically Black Colleges and Universities to claim leadership in one of the world’s most critical research frontiers.
When scientists like Alison Murray learned their Antarctic diving research would be indefinitely postponed due to the vessel withdrawal, it exposed a troubling reality: America is ceding scientific leadership in polar regions at precisely the moment when climate research has become existentially urgent. Yet within this crisis lies an opening that forward-thinking HBCU leaders and initiatives like the proposed HBCU Exploration Institute (HEI) should seize immediately.
The withdrawal of U.S. research capabilities from Antarctica isn’t happening in isolation. It reflects broader federal retreat from exploratory science across multiple domains from deep-sea mapping to atmospheric research to space exploration. As scientists told The Washington Post, building a replacement vessel could take years, leaving a generation of young researchers without access to critical field sites and diminishing American influence on a continent where geopolitical and scientific stakes are rising rapidly.
Currently, only a handful of nations operate dedicated Antarctic vessels capable of navigating the continent’s treacherous ice-choked waters. As America pulls back, countries including China, Russia, and even smaller nations are expanding their polar research fleets and infrastructure. This isn’t merely about scientific prestige it’s about who shapes climate policy, who controls access to research sites, who sets international standards for environmental stewardship, and ultimately, who benefits from discoveries made in these frontier regions.
For HBCUs, this federal abandonment creates a three-fold opportunity: to fill genuine research gaps with immediate societal value, to establish institutional leadership in high-stakes scientific domains, and to fundamentally reframe the narrative about who leads exploration and discovery in the 21st century.
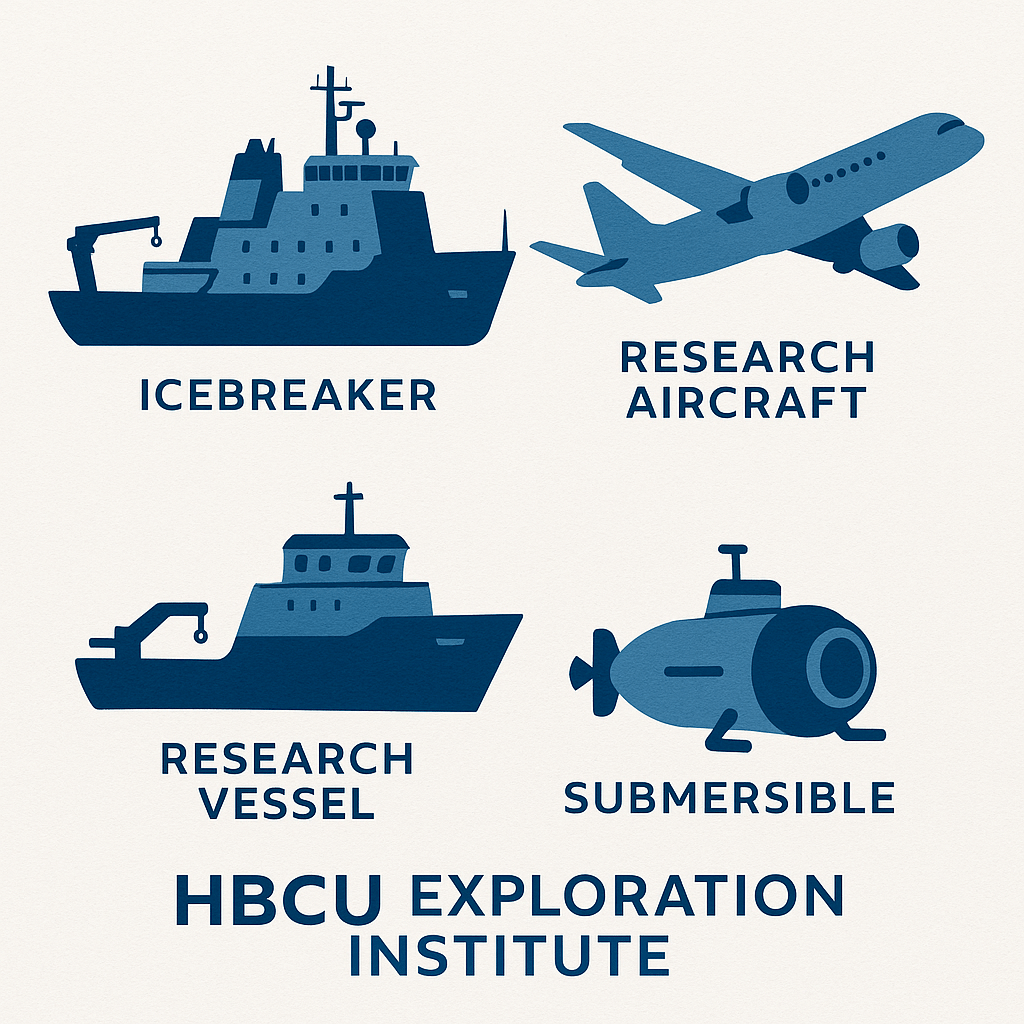
The HBCU Exploration Institute concept outlined in its founding business plan isn’t simply about participating in exploration it’s about transforming who controls the means of discovery. The proposed organization would operate research vessels, aircraft, field stations, and space payloads governed and staffed by HBCU talent, creating a parallel infrastructure to traditional federal research systems. This model offers several strategic advantages in the current moment. First, HBCUs can move with greater institutional agility than large federal bureaucracies. While government agencies debate budget allocations and political appointees shift priorities with each administration, a Pan-African, HBCU-led exploration organization could secure diverse funding streams—from philanthropic foundations to international partnerships to corporate sponsors—that insulate research from political winds.
HBCUs bring essential perspectives to exploration science that mainstream institutions have historically marginalized. The concept of “exploration power” examining whose data is gathered, who gathers it, and who benefits is central to HEI’s mission. This isn’t abstract ethics; it’s practical strategy. Research conducted in partnership with African and Caribbean institutions, for example, can build diplomatic relationships and shared intellectual property frameworks that strengthen both African American and African Diaspora scientific capacity. The HBCU network represents untapped human capital. Talented Black students and faculty have faced persistent barriers to entry in traditional exploration fields, from oceanography to aerospace. An HBCU-led initiative could create direct pipelines from undergraduate research to polar expeditions to faculty positions, bypassing gatekeeping mechanisms that have kept exploration science predominantly white and economically privileged.
Perhaps most significantly, launching an HBCU exploration initiative at this moment positions these institutions as leaders not just in American higher education, but within the global African diaspora’s intellectual ecosystem. African and Caribbean nations are rapidly expanding their own scientific capabilities. The African Union Space Agency, launched in recent years, coordinates satellite programs and space research across the continent. Caribbean nations are investing in climate resilience research essential to their survival. Yet many of these institutions lack the infrastructure, funding, and international partnerships that even modestly-resourced American HBCUs can access.
An HBCU Exploration Institute operating polar icebreakers, conducting deep-sea research, and launching satellite payloads wouldn’t just advance American science it would establish HBCUs as anchor institutions for Pan-African scientific collaboration. Imagine Howard University leading joint oceanographic research with the University of Ghana, or Spelman College coordinating atmospheric monitoring stations across the Caribbean. The reputational gains would be transformative. This matters for recruitment, fundraising, and influence. Prospective students choosing between HBCUs v. PWIs would see real HBCU ships, real HBCU expeditions, and real HBCU career pathways into exploration science. Donors and foundations seeking to support climate research and diversity initiatives simultaneously would find a natural home. And HBCU presidents would have new platforms for thought leadership on issues from climate power to space policy to scientific diplomacy.
Here’s an uncomfortable truth: this initiative will only succeed if HBCU alumni associations mobilize with the same intensity, pride, and financial commitment they bring to homecoming football games and basketball tournaments. Every fall, HBCU alumni pour millions into athletics for season tickets, tailgate sponsorships, facility upgrades, coaching staff salaries. Alumni associations organize elaborate events, coordinate donor campaigns, and celebrate athletic achievements with genuine institutional pride. The Battle of the Real HU generates more alumni engagement and media attention than most academic programs receive in a decade. That energy, that organizational capacity, that willingness to invest must now be redirected toward exploration science with the same fervor.
Imagine if Howard University’s alumni association launched a “Name a Research Station” campaign with the same production value as a homecoming concert. Picture Spelman graduates organizing Antarctic expedition watch parties with the same enthusiasm as NCAA tournament viewing events. Envision FAMU’s National Alumni Association creating an “Explorers Circle” giving society that receives the same social prestige as premium athletic booster clubs. This isn’t criticism of HBCU athletics culture it’s a call to expand that culture to encompass scientific exploration. The infrastructure already exists. Alumni associations know how to run capital campaigns, coordinate reunion giving, leverage social networks, and create moments of collective pride. These skills transfer directly to funding research vessels and field stations.
The proposed HBCU Exploration Institute requires $102 million over three years. That sounds daunting until you consider that HBCU athletic programs collectively generate hundreds of millions annually, most of it from student fees. A coordinated campaign across major HBCU alumni networks—Howard, Spelman, Morehouse, Hampton, Tuskegee, FAMU, North Carolina A&T, Southern, Jackson State, Prairie View A&M—could realistically raise $25-30 million in year one if alumni leadership treats this with athletic-level urgency. Some institutions have already demonstrated this model. When North Carolina A&T needed to upgrade its engineering facilities, alumni responded with major gifts because they understood engineering excellence as core to institutional identity. Spelman’s alumni have funded science facilities and research programs. But these efforts have remained institution-specific and episodic. What’s needed now is collective, sustained mobilization.
Alumni associations must take several concrete actions immediately. First, every major HBCU alumni organization should establish an Exploration Science Committee with the same organizational status as athletic support committees. These groups would coordinate giving campaigns, identify potential major donors from alumni ranks, and create visibility for exploration research. Second, alumni homecoming and reunion events must begin celebrating scientific exploration with the same pageantry as athletics. Feature returning researchers presenting expedition findings. Honor alumni working in climate science, oceanography, and aerospace with the same recognition as athletic hall of fame inductees. Create traditions around scientific achievement that become part of institutional identity.
Third, alumni networks must leverage their professional positions to open doors. HBCU graduates work throughout corporate America, foundation leadership, and government agencies. An organized alumni effort could secure corporate sponsorships, foundation meetings, and federal partnership discussions that individual institutions struggle to access. When Hampton alumni at NASA advocate for HBCU partnerships, or Spelman graduates at the Mellon Foundation champion exploration science grants, institutional barriers dissolve. Fourth, alumni giving must be restructured to prioritize exploration infrastructure. Many alumni give to scholarship funds or general operating budgets, which is valuable but doesn’t build transformative capacity. Alumni associations should create specific endowments for vessel operations, expedition funding, and fellowship programs—tangible assets that generate sustained visibility and research output.
The cultural shift required is significant but not unprecedented. HBCU alumni already understand institutional pride, collective identity, and the power of coordinated action. They’ve built that culture around athletics because athletics has been positioned as central to HBCU identity and excellence. Exploration science must now be positioned the same way. This means changing the narrative from “HBCUs need better STEM programs” to “HBCUs will lead humanity’s next era of discovery.” It means alumni bragging about their school’s Antarctic expedition with the same pride they show for conference championships. It means young alumni seeing paths to exploration careers at their alma maters, not just at mainstream institutions.
The financial model becomes achievable when viewed through this lens. If each of the top 20 HBCU alumni associations committed to raising just $5 million over three years for exploration science—less than many spend on athletic facility upgrades—the startup capital is secured. Add foundation grants and federal partnerships, and the budget is covered. But more than money, alumni provide legitimacy, momentum, and accountability. When alumni demand progress on exploration science initiatives with the same intensity they demand winning seasons, institutional leadership responds. When alumni celebrate research expeditions with the same enthusiasm as rivalry games, prospective students take notice. When alumni networks coordinate giving and advocacy, transformation becomes possible.
The HEI business plan proposes a $102 million startup budget over three years to acquire vessels, establish field stations, fund expeditions, and build fellowship programs. That’s substantial, but it’s also achievable given current philanthropic interest in both climate research and HBCU development. The Bezos Earth Fund has committed billions to climate research. The Mellon Foundation has prioritized HBCU infrastructure investment. NASA and NOAA, despite federal constraints, actively seek diverse institutional partnerships. A well-organized HBCU consortium could secure multi-year commitments from these sources, particularly by framing the initiative as addressing federal research gaps.
The immediate focus should be marine research, where the vessel shortage is acute. Acquiring or leasing even one ocean-capable research ship—potentially a refitted commercial vessel—would allow HBCUs to begin Antarctic and Arctic research within two years rather than waiting for federal capacity to rebuild. Partnering with international research programs could offset operational costs while building the diplomatic relationships that strengthen HBCU global standing. Field stations in strategic locations like the Gulf Coast, Alaska, Ghana, the U.S. Virgin Islands would serve multiple functions: research platforms, student training sites, and hubs for international collaboration. These don’t require massive funding; even modest facilities become transformative when they provide HBCU students access to environments and equipment unavailable on their home campuses.
The fellowship and expedition programs are equally critical. Summer research academies focusing on polar, marine, and aerospace exploration would create immediate visibility and impact. Graduate fellowships with guaranteed expedition participation would attract top-tier students who might otherwise choose mainstream programs. Faculty sabbaticals at international field sites would bring research capacity and publications that elevate institutional rankings.
Predictable objections will emerge: HBCUs lack the expertise, the infrastructure, the established research networks. But these arguments mistake historical exclusion for inherent incapacity. HBCUs have produced astronauts, oceanographers, and polar scientists they’ve simply done so while their parent institutions received minimal support for exploration science infrastructure. Moreover, the proposed model explicitly builds on existing strengths. Many HBCUs have robust Earth science, environmental science, and physics programs that lack only field research opportunities. The institute wouldn’t create scientific capacity from nothing; it would provide the ships, stations, and funding to activate capacity that already exists but remains underutilized. The real risk isn’t that HBCUs might fail at exploration science it’s that by not trying, they’ll watch other institutions and nations claim leadership in domains that will define 21st-century research prestige and funding.
Federal withdrawal from Antarctic research won’t reverse quickly. Budget constraints, political dysfunction, and competing priorities mean the vessel gap could persist for a decade or more. That timeline perfectly matches the HEI five-year development plan, which envisions operational vessels and field stations by year three and landmark research publications by year four. HBCUs face a choice. They can wait for federal capacity to rebuild, competing for scarce berths on research vessels if and when they return to service. Or they can recognize this moment as the opportunity it is: a chance to build independent exploration infrastructure, establish diaspora research leadership, and fundamentally shift the narrative about who belongs in humanity’s most ambitious scientific endeavors.
But this choice isn’t just for presidents and administrators it’s for the millions of HBCU alumni whose collective power remains largely untapped for scientific advancement. The same alumni networks that fill stadiums, fund athletic scholarships, and travel across the country for homecoming games must now channel that organizational capacity toward building research fleets and exploration programs. The motto proposed for the HBCU Exploration Institute is “To Discover, To Lead, To Belong.” That sequence matters. Discovery creates the intellectual foundation. Leadership transforms institutions and influences policy. But belonging establishing permanent presence in exploration science requires infrastructure, commitment, and the willingness to act when opportunities emerge.
America’s retreat from Antarctica isn’t just a setback for researchers like Alison Murray. It’s an invitation for institutions that have been systematically excluded from exploration science to step forward and claim the leadership role they’ve always been capable of holding. The question is whether HBCU leaders and, crucially, whether HBCU alumni will recognize this moment and seize it before it passes. The energy, pride, and resources are already there mobilized. Now they must be redirected toward putting HBCU names on research vessels sailing to Antarctica, field stations conducting climate research, and satellite payloads orbiting Earth. That’s a legacy worth more than any championship trophy.