“If you don’t find a way to make money while you sleep, you will work until you die.” — T. Harv Eker
In the American imagination, wealth is often synonymous with work—grit, grind, and the relentless pursuit of the paycheck. Yet the country’s richest families rarely labour for their living. Their fortunes compound quietly, buoyed by investments, dividend-paying stocks, real estate, and business interests. For Black households, whose median net worth remains a fraction of their white counterparts, accessing such passive income streams remains a frontier of both opportunity and historical consequence.
According to recent data from the U.S. Census and the Federal Reserve, only 7% of Black households report receiving passive income—whether from rental properties, interest, dividends, or business ownership—compared to 24% of white households. And when such income does exist, the median amount for Black families barely touches $2,000 annually, compared to nearly $5,000 for white households. This income disparity is not incidental. It reflects generations of exclusion, underinvestment, and systemic barriers to asset ownership.
But it is changing.
Across the U.S., a growing cohort of Black investors, entrepreneurs, and financial organizers are working to reverse this trend. From stock investing circles to community real estate funds and digital asset education, there is an awakening to the principle that “money must work when we do not.”
A Quiet Crisis in the Wealth Equation
Wealth in America has never been evenly distributed, but the passive income gap underscores a more insidious asymmetry: not just what people earn, but how money is multiplied. For much of the 20th century, Black Americans were systematically denied access to the very tools that compound wealth. Home loans were redlined. Stock brokers ignored Black neighborhoods. Black-owned businesses were underfinanced and over-regulated.
“We talk a lot about income inequality, but asset inequality is far more dangerous,” says Dr. Lenora Matthews, professor of finance at Howard University. “Passive income is how wealth survives across generations. Without it, every dollar must be earned, every month restarted from zero.”
The result has been a fragile wealth ecosystem. Black households are more likely to rely solely on wages, less likely to inherit financial assets, and more burdened by student debt. This combination severely limits participation in the capital markets that fuel passive income.
Enter the Index Fund
Among the most accessible starting points for passive income is the stock market—particularly index funds and ETFs (exchange-traded funds). These instruments offer low-cost, diversified exposure to the market and require little financial sophistication.
Platforms like M1 Finance, Public, and Fidelity now allow investors to buy fractional shares, meaning a person can invest $10 into the S&P 500 rather than $500 for a single share. Many Black investors are leveraging this entry point to build long-term portfolios with monthly contributions.
Tasha McDaniel, a teacher in Atlanta, began investing during the pandemic with just $50 per paycheck. “I never thought I’d be an investor,” she says. “But I realized my savings account was losing to inflation. Now my dividends buy more shares automatically.”
Her strategy follows a principle now gaining traction in Black financial circles: automatic reinvestment. Known as DRIP (Dividend Reinvestment Plan), it ensures that dividend payments purchase additional shares—compounding returns without additional cash input.
Real Estate: The Tangible Asset
Beyond equities, real estate remains the second pillar of passive income strategy. But here too, Black households have been historically marginalized. In 2022, the Black homeownership rate stood at 44%, compared to 74% among whites, a gap wider than it was in 1968 when the Fair Housing Act was passed.
And yet, platforms like Roofstock, Fundrise, and Arrived Homes are lowering the barriers. These services allow users to invest in rental properties, either fractionally or outright, while property management is handled externally—turning what was once an intensive business into a hands-off income stream.
“There’s a myth that you need $100,000 to buy a rental,” says Marcus Green, a Detroit-based real estate investor. “But with the right markets and leveraging community capital, Black investors can and are buying back the block.”
Indeed, co-investment models are growing. In cities like Birmingham, Baltimore, and Chicago, Black investment clubs are pooling resources to purchase duplexes and small multi-family homes. Each investor receives a percentage of rental income, and over time, equity appreciation.
The model is not new. It mirrors how Jewish, Chinese, and Caribbean diasporas historically approached real estate. What is new is the technological infrastructure allowing even small investors to participate.
Business Ownership: The Third Rail
Owning a business is arguably the most lucrative form of passive income—especially if it can be structured to run without the founder’s daily involvement. But again, Black entrepreneurs face outsized barriers. A 2021 Brookings report found that Black-owned businesses are half as likely to receive funding and receive only a third as much capital, even when creditworthiness is equal.
Still, entrepreneurship remains a favored strategy. Digital businesses—especially those selling information products, such as eBooks, online courses, or print-on-demand merchandise—offer high margins with low startup costs.
“I created a personal finance course for new parents,” says Jamal Pierce, a Houston-based father of two. “It took me three weekends. Now it makes $500 a month, and I haven’t touched it in a year.”
Similarly, Black creators on platforms like YouTube, Etsy, and Substack are finding ways to turn knowledge, creativity, and community into automated income. While these streams begin modestly, they represent a critical shift: from hourly labor to scalable value.
Trust, Trauma, and Financial Literacy
While access to capital is critical, trust and cultural engagement are equally important. Surveys consistently show that Black Americans are less likely to trust financial institutions. This distrust is not irrational. From the exploitation of Freedman’s Bank to discriminatory banking practices in the 2000s housing crash, history abounds with financial betrayal.
To bridge this gap, a new generation of Black financial educators is emerging. TikTok influencers, YouTube educators, and community workshops are now teaching passive income strategies with a culturally relevant lens.
“Financial literacy must come from trusted voices,” says Ayana Holland, founder of Black Wealth Book Club. “We aren’t just teaching stocks; we’re healing financial trauma.”
Her organization hosts monthly readings and investment challenges, helping members open brokerage accounts, buy dividend-paying stocks, and learn the language of capital.
Group Economics Reimagined
One of the most powerful but underutilized tools in the Black community remains cooperative economics. The tradition of “sou-sous” and rotating savings clubs dates back centuries but is now being modernized into investment syndicates and real estate cooperatives.
In New York, the Umoja Investment Circle—formed by five Black women—collectively saved $60,000 in a year and used it to buy a cash-flowing rental property in upstate New York. Each member now receives quarterly dividends.
“We realized we didn’t need to wait for the bank,” says founding member Tiffany Rhodes. “We were the capital.”
Such models not only build wealth but restore a sense of agency and interdependence. They allow families and communities to reclaim the capital flight that has plagued Black neighborhoods for decades.
Digital Assets and the Cautionary Horizon
The emergence of digital assets, particularly cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi), has sparked curiosity and concern among Black investors. On one hand, Black Americans have adopted crypto at faster rates than their white peers, drawn by its decentralization and promise of wealth democratization.
On the other, the market’s volatility and regulatory uncertainty pose significant risks. The collapse of platforms like FTX and Celsius has reignited warnings about speculation without education.
“Crypto is not the enemy,” says Kaylin James, a blockchain consultant. “But we must separate hype from fundamentals. Bitcoin can be a long-term store of value, but not every coin is your ticket to freedom.”
The lesson is clear: passive income must be built on understanding, not urgency.
Policy Interventions and Structural Change
While individual strategies matter, structural change is essential to closing the passive income gap. Federal and state policies must expand access to retirement accounts, support first-time homebuyers, and fund Black-owned startups.
Programs like baby bonds, universal 401(k) participation, and public banking could democratize the tools of wealth. So too could the strengthening of historically Black financial institutions—credit unions, community development financial institutions (CDFIs), and HBCU endowments.
Indeed, institutions like OneUnited Bank and the HOPE Credit Union are already deploying capital into underserved areas, while crowdfunding models like Black Wall Street Cooperative are testing new modes of community finance.
Toward Financial Sovereignty
The quest for passive income is not merely a financial ambition—it is a reclaiming of time, dignity, and possibility. For Black households, it represents both survival and sovereignty. It is the freedom to plan, to rest, and to invest in future generations.
In a world where work grows ever more precarious and inequality more entrenched, the ability to earn without labour is no longer a luxury. It is an imperative.
As Jamal Pierce puts it: “I don’t want my kids to inherit hustle. I want them to inherit options.”
The shift is underway. The movement is growing. Passive income is not a dream. It is a strategy—and a declaration—that Black wealth will not be denied, only delayed.

Analysis with Focus on African Americans
The chart presents data on median passive income and the percentage of households with passive income across different racial/ethnic groups. Here’s a focused analysis on African Americans (Black households) in comparison to others:
Passive Income Levels
- Black households have the lowest median passive income compared to other groups.
- Their median passive income is around $2,500, significantly lower than White, Hispanic, and Asian households, which are all above $4,000.
- This suggests that Black households have less access to wealth-generating assets such as investments, rental properties, and other income-generating financial vehicles.
Percentage of Households with Passive Income
- Black households also have the lowest percentage of households receiving passive income (approx. 6%).
- This is significantly lower than Non-Hispanic White and Asian households, indicating that fewer Black families are benefiting from income streams outside of wages and salaries.
- The disparity may be linked to historical and systemic barriers to wealth accumulation, including lower rates of homeownership, limited access to capital for investments, and disparities in inheritance.
Comparative Insights
- Hispanic households, despite having near the same percentage of households receiving passive income as Black households, have a relatively equal median passive income to White and Asian households with White, Asian, and Hispanic households median passive income being over 50 percent greater than African American households.
- In contrast, Non-Hispanic White and Asian households have both a higher proportion of households with passive income and significantly higher median passive income, suggesting a stronger institutional wealth advantage.
- The data reinforces broader economic research that points to racial wealth gaps in the U.S., where Black families historically have had fewer opportunities to build wealth post World War II due to the G.I. Bill and desegregation leading to the demolishing of African American institutional wealth.
Potential Implications & Solutions
- Financial literacy & investment education: Increasing awareness and access to investment opportunities can help improve passive income for Black households.
- Wealth-building programs: Policies aimed at reducing barriers to property ownership and business investment can support long-term financial stability.
- Access to capital: Expanding access to business loans, stock market investments, and other wealth-building tools can improve financial mobility.

Additional Insights on Passive Income Disparities for Black Households
Building on the previous analysis, let’s explore some deeper economic, historical, and structural factors that contribute to the lower levels of passive income among Black households.
Historical Barriers to Wealth Accumulation
- Redlining & Housing Discrimination:
- Homeownership is a key driver of wealth in the U.S. Black Americans were historically excluded from homeownership through redlining, restrictive covenants, and discriminatory lending practices.
- Even today, Black homeownership rates remain significantly lower, limiting the ability to build home equity that could generate rental income or be passed down to future generations.
- Limited Access to Financial Markets:
- Generational wealth disparities mean Black families are less likely to inherit assets such as stocks, bonds, or investment properties.
- The racial wealth gap reduces the ability to invest in income-generating assets like rental properties, mutual funds, or businesses.
Income vs. Wealth: Why This Matters for Passive Income
- Higher Reliance on Earned Income:
- The data suggests that Black households rely more on wages and salaries rather than passive income streams.
- Without accumulated wealth or financial investments, it becomes harder to transition from relying solely on wages to generating income passively.
- Debt Burden & Financial Constraints:
- Black households tend to carry higher levels of student loan debt relative to income.
- This reduces disposable income that could otherwise be invested in wealth-generating assets like stocks, businesses, or real estate.
Entrepreneurship & Business Ownership
- Lower Rates of Business Ownership:
- Business ownership is a major source of passive income, yet Black entrepreneurs face systemic barriers to access funding.
- According to studies, Black business owners are more likely to be denied loans or receive less funding than White business owners with similar qualifications.
- The lack of capital prevents many Black entrepreneurs from scaling their businesses into passive income-generating enterprises.
Investment Disparities
- Lower Stock Market Participation:
- Stock investments are a major source of passive income (dividends, capital appreciation).
- Research shows that Black Americans are less likely to invest in the stock market, often due to financial constraints, lack of investment knowledge, or distrust in financial institutions.
- This contributes to the income gap, as wealthier groups benefit disproportionately from stock market growth.
- Retirement Savings Gap:
- Black workers are less likely to have employer-sponsored retirement accounts such as 401(k) plans, which can serve as passive income sources later in life.
- Lower contributions to retirement accounts also mean reduced wealth accumulation over time.
Policy & Structural Solutions
To address these disparities, several targeted interventions could help increase passive income opportunities for Black households:
✅ Financial Education & Investment Access:
- Expanding financial literacy programs to educate communities about investing, real estate, and wealth-building strategies.
- Encouraging early participation in retirement and investment accounts.
✅ Homeownership Support:
- Strengthening first-time homebuyer assistance programs for Black families to increase homeownership rates.
- Expanding access to fair lending and mortgage assistance programs.
✅ Entrepreneurship & Capital Access:
- Increasing access to venture capital and business loans for Black entrepreneurs.
- Expanding mentorship programs that connect Black business owners with experienced investors.
✅ Workplace & Policy Interventions:
- Strengthening retirement benefits and employer-matching programs.
- Enforcing anti-discrimination laws in financial institutions to ensure fair lending practices.
The chart illustrates a clear racial disparity in passive income, which is a key driver of long-term financial stability. Addressing this gap requires both individual financial strategies and systemic policy changes to create more equitable opportunities for Black households to build and sustain wealth.
Investment Strategies for Building Passive Income in Black Households
Building passive income requires a strategic approach to investing, asset accumulation, and financial planning. Here are some tailored investment strategies that can help Black households increase wealth and long-term financial stability.
Stock Market Investing (Long-Term Wealth Growth)
Investing in the stock market is one of the best ways to generate passive income through dividends and capital appreciation.
How to Get Started:
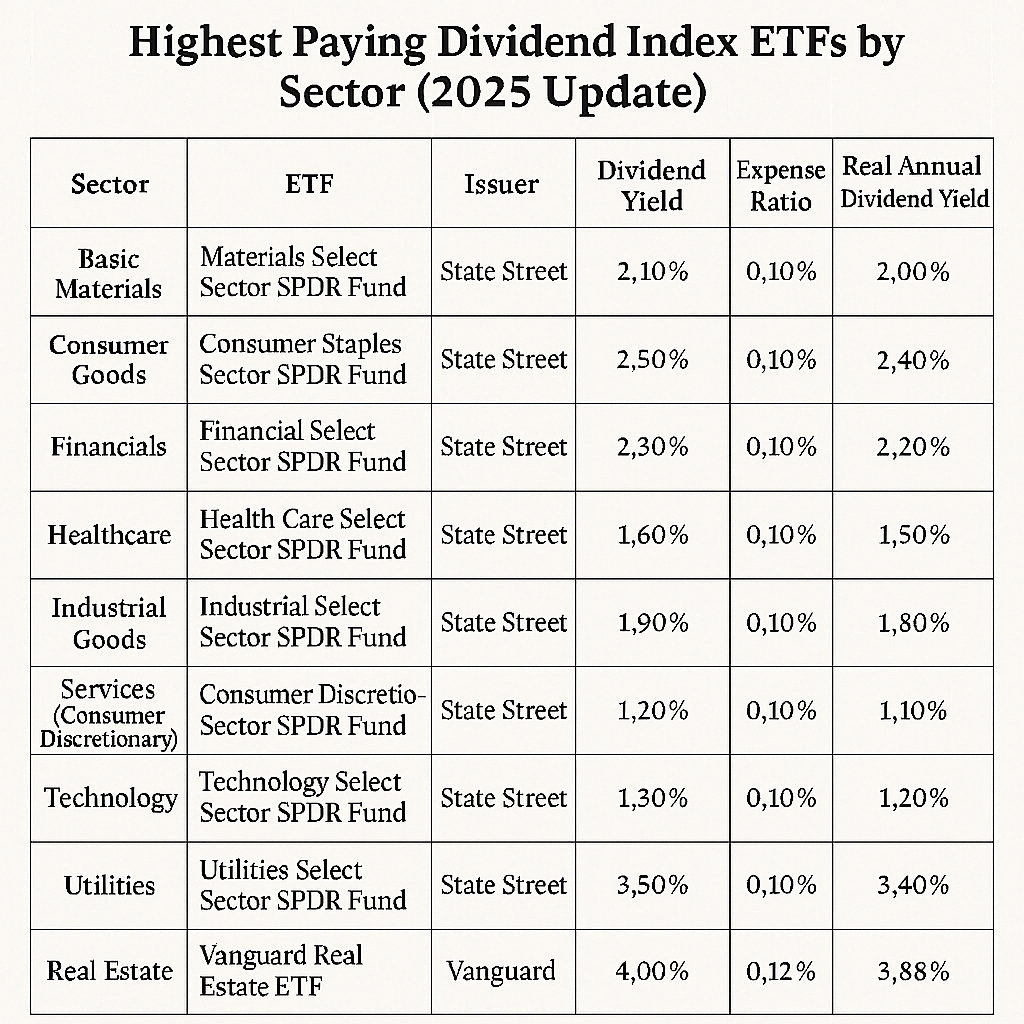
✅ Invest in Index Funds & ETFs:
- Index funds (e.g., S&P 500) and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) offer diversification and long-term growth with minimal risk.
- Example: Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI), SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY), or Fidelity Zero Large Cap Index Fund (FNILX).
✅ Dividend Stocks for Passive Income:
- Some stocks pay dividends, providing consistent cash flow.
- Examples: Johnson & Johnson (JNJ), Coca-Cola (KO), Procter & Gamble (PG).
- Consider Dividend ETFs like Vanguard Dividend Appreciation ETF (VIG).
✅ Start Small & Use Fractional Shares:
- Apps like Robinhood, M1 Finance, and Fidelity allow investing with as little as $5.
- Investing in fractional shares lets you own expensive stocks (e.g., Amazon, Apple) without needing full stock prices.
✅ Retirement Accounts for Tax Advantages:
- 401(k) or 403(b) Plans (if employer-sponsored) – Max out contributions, especially if there’s an employer match.
- Roth IRA or Traditional IRA – Tax-free or tax-deferred investment growth.
Real Estate Investing (Building Generational Wealth)
Real estate is a powerful way to create passive income and build long-term wealth.
Ways to Invest in Real Estate:
🏡 Rental Properties (Buy & Hold Strategy):
- Purchase properties in high-growth areas and rent them out.
- House-hacking: Buy a duplex, live in one unit, and rent the other to cover your mortgage.
🏘 Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) (For Hands-Off Investing):
- REITs allow you to invest in real estate without owning property.
- They pay out dividends and grow in value over time.
- Examples: Vanguard Real Estate ETF (VNQ), Realty Income Corp (O).
🏗 Short-Term Rentals (Airbnb, VRBO):
- Renting out a portion of your home or a property on Airbnb can generate passive income.
🏠 Crowdfunded Real Estate:
- Platforms like Fundrise, Roofstock, and RealtyMogul let you invest in real estate with as little as $500.
Entrepreneurship & Online Business (Creating Scalable Income)
Starting a business can provide long-term passive income if structured correctly.
Low-Cost Online Business Ideas:
💻 Create Digital Products (eBooks, Courses, Templates):
- Platforms like Gumroad, Teachable, and Udemy allow you to sell digital products with no inventory costs.
🎙 Monetize Content (YouTube, Blogging, Podcasting):
- Ad revenue, affiliate marketing, and sponsorships can generate passive income over time.
- Example: Start a finance blog, career coaching YouTube channel, or real estate investing podcast.
📈 Affiliate Marketing & Dropshipping:
- Promote other brands’ products and earn commissions without handling inventory.
- Use platforms like Amazon Associates, Shopify, and ClickBank.
Passive Income from Bonds & Fixed-Income Investments
Bonds provide steady income with lower risk than stocks.
Best Bond Investments:
📜 U.S. Treasury Bonds & I Bonds:
- Safe and backed by the government.
- I Bonds protect against inflation and currently offer high-interest rates.
🏦 Corporate Bonds & Municipal Bonds:
- Corporate bonds pay higher interest but carry slightly more risk.
- Municipal bonds offer tax-free income and are great for long-term wealth preservation.
📊 Bond ETFs for Diversification:
- Example: Vanguard Total Bond Market ETF (BND).
Community & Group Investing (Building Wealth Collectively)
Pooling resources can help overcome capital barriers in investing.
How to Invest as a Group:
👥 Investment Clubs & Stock Groups:
- Join or create an investment group to collectively buy stocks or real estate.
- Apps like Public and M1 Finance allow social investing.
🏡 Real Estate Syndication & Co-ops:
- Partner with others to invest in properties together.
- Example: Several families invest in an apartment complex and split the rental income.
🌍 Peer-to-Peer Lending (P2P):
- Platforms like LendingClub allow investing in loans for passive interest income.
Leveraging Technology & Automation for Passive Income
📲 Set Up Automated Investing:
- Use Robo-Advisors (Wealthfront, Betterment) for hands-off investing.
- Set up automatic dividend reinvestments (DRIP) to grow wealth faster.
📱 Passive Income Apps:
- Honeygain & Nielsen Rewards: Earn passive income by sharing internet bandwidth.
📈 Side Hustles with Passive Potential:
- Print-on-Demand (Etsy, Redbubble)
- Amazon Kindle Direct Publishing (KDP)
Final Takeaways: Actionable Steps
🔹 Step 1: Open a brokerage account (Fidelity, Vanguard, or Charles Schwab) and start investing in stocks, ETFs, or REITs.
🔹 Step 2: If possible, buy a rental property or start with REITs for real estate exposure.
🔹 Step 3: Automate savings & investments through 401(k), Roth IRA, or Robo-advisors.
🔹 Step 4: Explore low-risk passive businesses.
🔹 Step 5: Consider group investing with family or community investment clubs.