
At close of market May 16th, 2025 Carver Federal Savings Bank (Ticker: CARV) stock price was $1.37 and had a market capitalization of $7 million.
In the heart of Harlem, a modest stone building bears a powerful legacy. Carver Federal Savings Bank, founded in 1948 to serve African Americans shut out of the financial system, once stood as a proud monument of Black economic independence. But more than a decade after a series of financial interventions shifted its ownership structure, Carver remains out of African American hands—raising questions about the future of Black-owned banking in America’s largest city.
For much of the 20th century, Carver Federal Savings Bank wasn’t just a bank—it was a symbol. Born in the crucible of racial segregation, the bank was named after George Washington Carver, a gesture toward economic empowerment and self-reliance in an era when African Americans couldn’t freely access mortgages, capital, or commercial loans. Carver stood apart as one of the few banks chartered to serve underserved Black communities with full-service financial products, not just basic deposit services. By the 2000s, Carver had grown into the largest Black-operated bank in the United States, holding nearly $800 million in assets and a footprint that extended across New York City. But the financial crisis of 2008 brought a devastating blow to community banks nationwide. Carver was no exception.
In 2011, to prevent collapse, Carver accepted a $55 million recapitalization led by Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, Citigroup, and Prudential Financial. The deal saved the institution from immediate failure but came with a price: Black ownership was diluted, and eventually disappeared altogether. “It was like watching a cultural landmark sold off piece by piece,” says Alfred Edmond Jr., senior vice president at Black Enterprise. The investors involved in the bailout argued that their capital preserved an essential community institution. Without it, Carver may have followed the path of other Black banks that shuttered in the wake of the crisis. Yet critics argue that Wall Street’s “rescue” functioned more as a quiet takeover.
As of 2024, Carver is publicly traded under the ticker symbol CARV on the NASDAQ. But its board of directors and major shareholders no longer reflect the community it was founded to serve. African American representation remains, but it is symbolic at best—not controlling. This is not merely symbolic loss. According to a 2023 Federal Reserve report, only 16 Black-owned banks remain in the United States—down from more than 50 in the 1990s. Black-owned banks hold less than 0.01% of America’s banking assets, despite African Americans comprising over 13% of the population. These institutions face outsized scrutiny, undercapitalization, and, more recently, cultural erasure. “Carver’s transformation reflects a broader systemic problem,” says Mehrsa Baradaran, professor of law and author of The Color of Money: Black Banks and the Racial Wealth Gap. “These banks are often asked to solve problems created by centuries of exclusion without the capital or autonomy to do so.”
In the wake of the George Floyd protests in 2020, corporate America made a wave of public commitments to racial equity. JPMorgan Chase pledged $30 billion. Bank of America committed $1 billion. A smaller yet symbolically important gesture came in the form of investments into Black-owned banks, often through special deposit programs or equity infusions. Carver, still labeled as a Minority Depository Institution (MDI), became the recipient of some of this renewed attention. Goldman Sachs’s One Million Black Women initiative included community bank support. JPMorgan made technical assistance available. But none of these efforts changed the fact that the bank was no longer under Black control. “The irony is that companies are promoting racial equity while owning and profiting from a once-Black institution,” says Nicole C. Elam, president and CEO of the National Bankers Association. “There’s no accountability mechanism to ensure community control is returned.” Despite all the attention, Carver’s stock remains volatile, trading below $4 per share for much of 2024. Its market capitalization hovers under $20 million—hardly a prize for large investors. And yet, efforts to return control to Black investors or the community have stalled.
At first glance, the logic is simple. If Black community leaders or financial institutions want Carver back, why not just buy it? The answer, as usual, lies in a thicket of regulatory burdens, capital constraints, and systemic inequities. First, buying back a publicly traded bank is not cheap. Not only must investors pay for the shares, they must also meet stringent capital adequacy standards, undergo intense scrutiny from the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) and the FDIC, and develop a viable turnaround plan. That requires not only money, but financial expertise and a willing group of institutional backers. Second, Black institutional capital remains relatively shallow. The combined assets of all Black banks in America are less than those of a mid-sized regional bank. Few HBCU endowments top $1 billion. Black venture capital and private equity firms are growing but still under-resourced. “If you don’t control the capital, you don’t control the bank,” says John Rogers Jr., founder of Ariel Investments. “And Black America still doesn’t have control of the capital.”
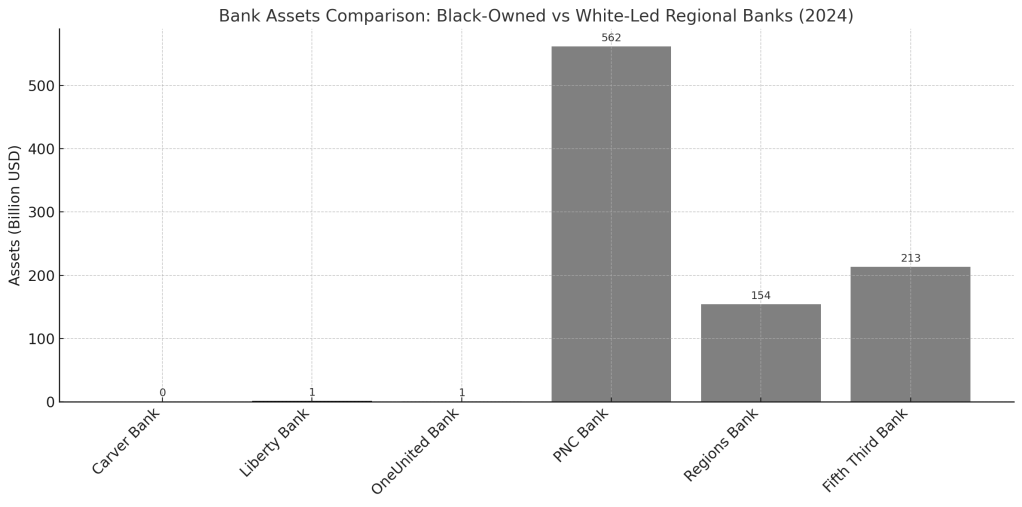
Some believe that the pandemic-era racial reckoning presented a missed opportunity. Corporate America was writing big checks. Foundations were searching for credible ways to support Black wealth-building. Influential Black philanthropists like Robert F. Smith and Mellody Hobson were encouraging long-term investments. With the right coordination, a capital stack combining philanthropy, mission-oriented investment, and community contributions could have reestablished Black control of Carver. But that coordination never materialized. “Institution building takes vision and orchestration. We had the moment. What we didn’t have was the mechanism,” says William Michael Cunningham, an economist and banking analyst. “Everyone wanted to help, but no one wanted to lead.”
New York’s political leadership has been largely silent on the issue. Harlem’s representation in the city council and state legislature rarely mentions Carver publicly. Even as the Adams administration touts equity initiatives and minority small business support, it has not made a coordinated effort to support community banking or institutional ownership transfer. Compare this to other minority community examples. In Chicago, the city has created a $100 million Community Wealth Fund to help finance minority entrepreneurs and institutions. In Atlanta, the Russell Center for Innovation and Entrepreneurship works closely with regional banks and city government to support Black business ecosystems. “New York talks a good game,” says Inez Barron, a former city councilmember. “But when it comes to economic infrastructure, the silence is deafening.”
The erosion of Black control of Carver has not gone unnoticed by its depositors. Harlem residents and small business owners say they still bank with Carver out of loyalty—but many no longer see it as their bank. “The staff are still great. The service is personal. But it doesn’t feel like we own it anymore,” says Celeste Washington, who owns a beauty salon two blocks from the 125th Street branch. “It feels like a museum of what Black finance used to be.” Others are more cynical. “It’s the same bank name, same building, but a different master,” says a former Carver employee who requested anonymity. “The soul’s been sold.”
Despite the challenges, some financial architects are working to engineer a return to community control. One idea gaining traction is a cooperative buyback. Using a vehicle similar to a special purpose acquisition company (SPAC), a collective of Black investors, philanthropists, and mission-driven capitalists could pool resources to buy out majority shareholders. A parallel idea involves transferring shares to a nonprofit trust governed by Harlem residents and business leaders. Others are pushing for a broader transformation of Black institutional capital. “We need to stop thinking of banks as only banks,” says economist Darrick Hamilton. “Think of them as economic platforms—distribution points for housing finance, entrepreneurship, education loans, and job creation. That’s what Carver could be again.” A Black-owned financial institution, particularly in a city as rich and diverse as New York, could be pivotal in building a community-centered economic ecosystem—from affordable housing cooperatives to small business lending networks to cultural real estate ownership.
Observers say that Black colleges and universities, especially those in the northeast like Howard University, Lincoln University (PA), and Morgan State, could play a strategic role. These institutions, along with Black philanthropic funds and pension boards, could pool endowment dollars to create an acquisition consortium. Even a modest $50 million fund could provide enough leverage to reclaim majority control and reorient Carver toward mission-driven service. “Imagine if Carver became the lead underwriter of mortgages for Black college alumni in major cities,” says Anthony Jackson, a Black banking consultant. “Or the back-end servicer of student loan refinancing for HBCU graduates. That kind of synergy could multiply.” The projected ROI on such a move isn’t trivial. Assuming a 10% annual return over 30 years, a $50 million investment grows to more than $872 million—more than the combined assets of most Black-owned banks today. It’s a long-term play—but one that offers strategic cultural, economic, and financial returns.
Carver’s story is still being written. It could continue as a bank preserved in name only, a hollowed-out shell of its former self. Or, with vision, coordination, and capital, it could return to its original purpose: not merely to serve Black communities, but to be owned by them. What’s at stake is more than a bank. It’s about ownership, power, and whether the symbols of Black advancement can be reclaimed—or will remain curated artifacts of a more ambitious past.
Disclaimer: This article was assisted by ChatGPT.
